August 26, 2023
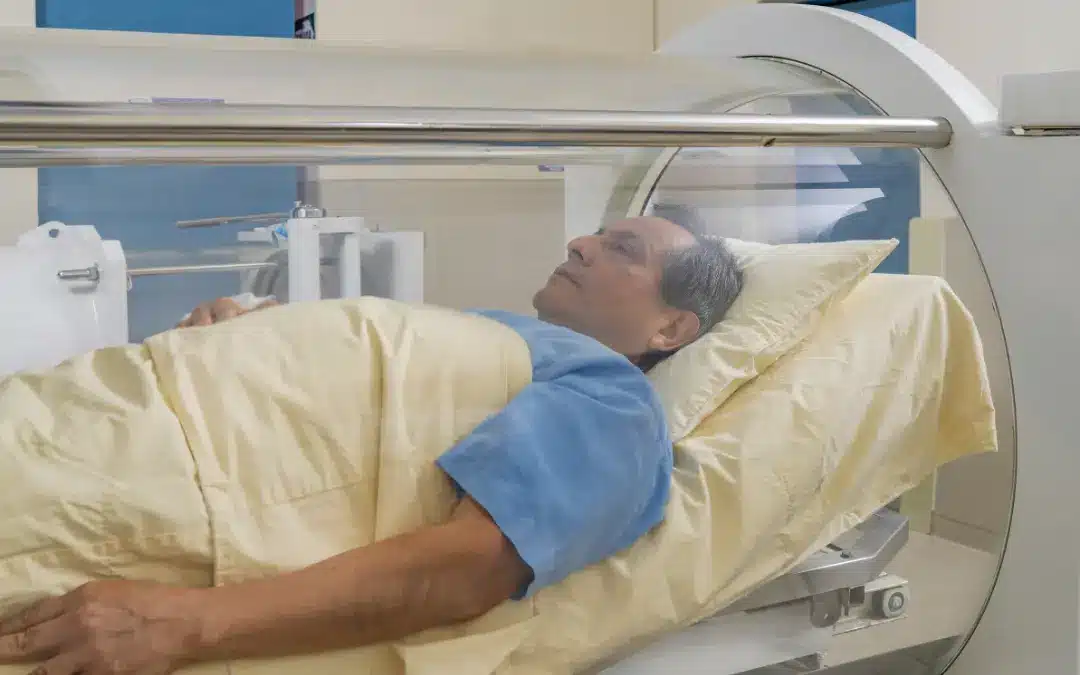
As the world grappled with the COVID-19 pandemic, medical researchers tirelessly explored various treatment options to alleviate the severe symptoms of the disease. In this article, we delve into a prospective, multi-centered, open-label randomized controlled study conducted by Dr. Cannellotto and colleagues, shedding light on the potential of hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO2) as an adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 patients with severe hypoxemia.
The COVID-19 pandemic presented an unprecedented challenge to the medical community, especially concerning patients experiencing severe hypoxemia, where oxygen saturation levels remained below 90% despite oxygen supplementation. Addressing this challenge required innovative approaches, and HBO research emerged as a potential solution, albeit often hindered by preconceptions and cost considerations.
Remarkably, this groundbreaking study was conducted in Argentina, despite the fact that the majority of COVID-19 patients and HBO2 chambers were located outside the country. Dr. Cannellotto and a dedicated team of clinicians sought to improve patient care during the pandemic while sharing their findings with the global medical community. Their commitment deserves applause.
To ensure the utmost safety of the participants, Cannellotto and colleagues carefully considered multiple factors related to COVID-19. They opted for a very low treatment pressure of 1.45 atmospheres absolute (ATA), a critical decision aimed at minimizing potential haemodynamic risks for the enrolled patients. For those less familiar with HBO2, it’s important to note that 1.45 ATA is the minimum pressure required for hyperbaric therapy.
The study included 40 patients, evenly split into two groups: 20 received HBO2 treatment, while the remaining 20 served as the control group without HBO2. All participants shared the common challenge of severe hypoxemia, making this research particularly relevant for addressing the critical needs of COVID-19 patients.
While the results of this study are yet to be fully disclosed, the mere exploration of HBO2 as an adjuvant therapy for severe COVID-19 hypoxemia is a significant step forward. By conducting well-designed research and challenging preconceptions about its utility, Dr. Cannellotto and his team have contributed to the global effort to combat the pandemic.
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the need for innovative approaches to patient care. Dr. Cannellotto and his colleagues have taken a bold step by investigating the potential of hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a supplementary treatment for severe COVID-19 hypoxemia. Their dedication to patient welfare and their commitment to sharing their findings pave the way for further exploration of HBO2 as a promising adjunctive therapy in the fight against COVID-19.
Kirby, J. (2021, October 1). Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for patients with COVID-19. Emergency Medicine Journal. https://emj.bmj.com/content/39/2/86
Share on:
A free, open discussion group to explore hyperbaric oxygen therapy, compare home chamber brands, access expert info, and get exclusive member discounts.